Spectral unmixing in R using RStoolbox
Recently, I finished the development of the first version of a spectral unmixing function being part of RStoolbox, an R package offering numerous tools for remote sensing analysis written by Benjamin Leutner. The multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (mesma) function makes it possible to unmix multi- and hyper-spectral imagery by sets of spectral endmember profiles. For this, a non-negative least squares (NNLS) solver was implemented. NNLS is a statistical approach to fit model parameters to data, assuming that the model parameters are always expressed linearly to those not expressed by the model (unknown parameters) and that the model parameters can never be negative. There are different approaches to solve the NNLS problem. A popular one had been introduced by Lawson & Hanson (1974), which can be considered as fundamental work on practical Least Square Problems solving. It was originally published as FORTRAN code, which is still widely used, e.g. by the R NNLS package or by the Python scipy library. However, compared to newer developing frameworks and languages emerged, the FORTRAN implementation is relatively slow. Thus and to be independent from existing solutions, I wrote a C++ NNLS solver for mesma(), based on a sequential coordinate-wise algorithm (SCA) introduced by Franc et al. (2005). The latter method inherits strong control about the solver’s iteration stopping conditions. Apart from NNLS, we are planning to add further solver methods (which is why I am currently looking for other practicable unmixing methods). In this post, I want to demonstrate, how to use the unmixing function RStoolbox::mesma() by giving an example. It can be reproduced on any device running R and having installed the current First, we are going to load the Landsat example imagery delivered with RStoolbox: To create some endmember spectra, we simply collect the spectral profiles of “water” and “land” from our imagery. We keep it simple here – instead, you could use spectra from a spectral library. That’s all for the pre-processing! Now you have an image and two endmembers. Note that you need to have at least two endmembers (as we have in this example) to unmix an image. Also, take a look at “em” and “lsat” before continuing: Both have the same spectral resolution (band number), which is a prerequisite. This means that if you want to use data from a spectral library for unmixing, you simply need to resample the data to the same spectral resolution of your imagery to use mesma(). Now, just call Since we decided to develop the NNLS solver from scratch in C++ and not to use existing older FORTRAN implementations, mesma() is quiet fast. It supports parallel processing, if you want to unmix large amounts of data and have multiple CPU cores available. To do so, just create a cluster before calling Now, let us look at the output’s with two simple two-coloured plots: and here they are for land: You clearly see, how References:
Franc, V., Hlaváč, V., & Navara, M. (2005). Sequential coordinate-wise algorithm for the non-negative least squares problem. In: International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns (pp. 407-414). Berlin, Heidelberg. Lawson, C. L., & Hanson, R. J. (1974). Solving least squares problems (Vol. 15). Siam. A similar version of this blog post has also been published at the webpage of the Department of Remote Sensing, University of Wuerzburg, Germany and at the EAGLE student’s webpage.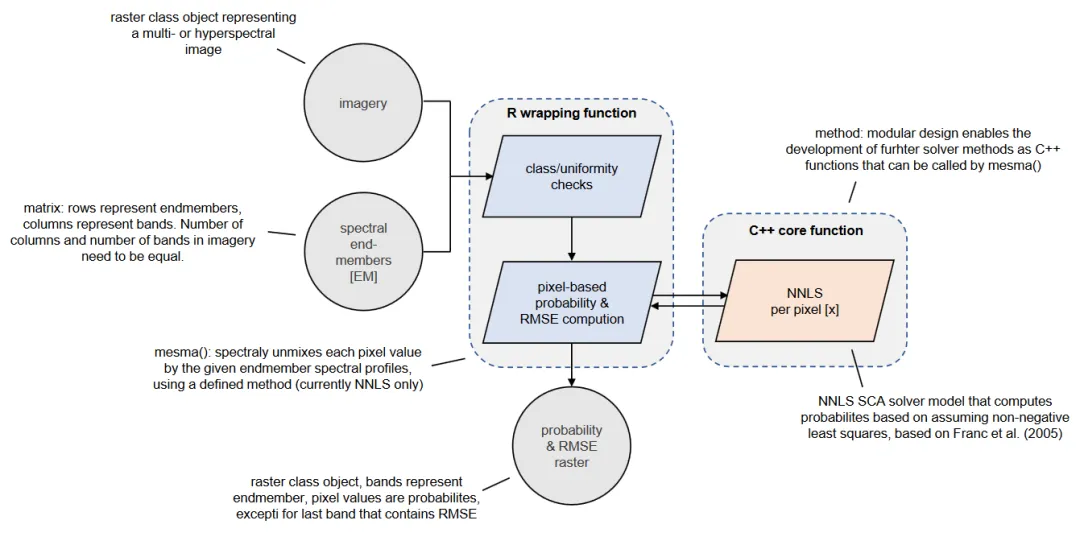
CRAN version of RStoolbox:install.packages("RStoolbox")#load packages
library(raster)
library(RStoolbox)
#load an example dataset
data(lsat)#make up some endmember spectra: water and land
em_names <- c("water", "land")
pts <- data.frame(class=em_names, cell = c(47916,5294))
em <- lsat[pts$cell]
rownames(em) <- em_namesmesma(). It returns a probability raster, each layer representing one class of your endmembers, except for the last layer, which gives you the RMSE for each pixel.#unmix the image for water and land
probs <- mesma(lsat, em, method = "NNLS")mesma() using raster::beginCluster() and stop it afterwards using raster::endCluster().
Here are the classified probabilities for water…
#' #take a look
raster::plot(probs$water, col = c("white","blue"))
raster::plot(probs$land, col = c("white","brown"))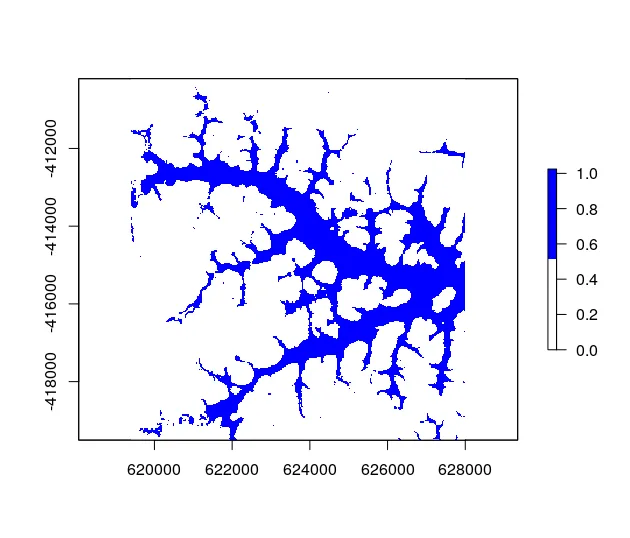
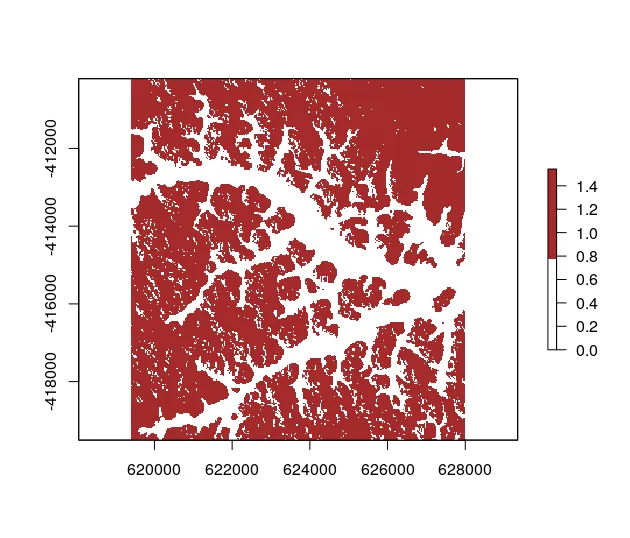
mesma() differentiated between these two endmembers with only one spectrum per class. If you have ideas or find a problem, please report us via GitHub.